Introduction to Svelte and SvelteKit
Let's Learn Svelte and SvelteKit.
Svelte vs SvelteKit - What’s the Difference?
If you’re learning Svelte, chances are you’ve also come across SvelteKit.
While the names are similar, they serve very different purposes.
In this post, we’ll explore the differences between Svelte and SvelteKit, when to use each, and why they matter in modern web development.
Svelte vs SvelteKit
The Svelte documentation explains it well. I’ll quote it directly.
Svelte renders UI components. You can compose these components and render an entire page with just Svelte, but you need more than just Svelte to write an entire app.
SvelteKit helps you build web apps while following modern best practices and providing solutions to common development challenges. It offers everything from basic functionalities — like a router that updates your UI when a link is clicked — to more advanced capabilities. Its extensive list of features includes build optimizations to load only the minimal required code; offline support; preloading pages before user navigation; configurable rendering to handle different parts of your app on the server via SSR, in the browser through client-side rendering, or at build-time with prerendering; image optimization; and much more. Building an app with all the modern best practices is fiendishly complicated, but SvelteKit does all the boring stuff for you so that you can get on with the creative part.
It reflects changes to your code in the browser instantly to provide a lightning-fast and feature-rich development experience by leveraging Vite with a Svelte plugin to do Hot Module Replacement (HMR).
To summarize:
Svelte is a open-source frontend framework that helps you build UI components easily. It’s suitable for small, simple projects or single-page applications.
SvelteKit is the official application framework** built on top of Svelte. It provides everything needed to build full-fledged applications, including routing, SSR(Server-Side Rendering), SSG(Static Site Generation), data fetching, and build optimization.
Introuduce Svelte
Svelte is an emerging frontend framework that has been gaining traction and growing rapidly following the rise of React and Vue. In modern web development, building everything solely with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is inefficient and time-consuming. That’s why developers turn to libraries and frameworks to streamline the process. Today, not only frontend development but the entire software ecosystem has become increasingly complex. Especially in the case of frontend frameworks, the abundance of options has created a significant learning curve for developers. Svelte aims to address this challenge and could be the solution to simplify frontend development.
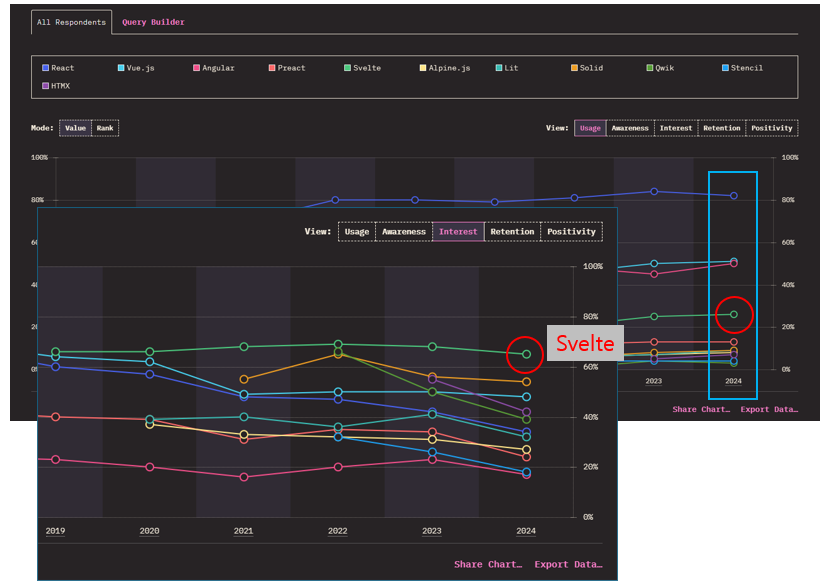 Frontend Framework(Source: Stateofjs)
Frontend Framework(Source: Stateofjs)
React vs Vue.js vs Svelte
| Framework | Features |
|---|---|
| React | The most widely adopted framework, known for its power and flexibility. Supports a vast ecosystem of libraries and tools. However, it comes with a relatively steep learning curve. |
| Vue.js | Easy to learn and beginner-friendly. Offers component-based development, making it easier to organize and manage code strategically. |
| Svelte | A fast and lightweight framework. Compiles to highly optimized JavaScript at build time, making it ideal for efficient development with minimal code. |
Each framework has its own strengths. If you want flexibility and community support, React is a solid choice. If you prefer simplicity and ease of use, Vue.js is worth considering. And if you’re looking for high performance with minimal complexity, Svelte might be the perfect fit.
The following code compares how to implement a button that increases the count value when clicked in React, Vue.js, and Svelte. As you can see, Svelte is noticeably more concise and simple compared to the others.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
<!-- React -->
import React, { useState } from 'react'
export const CounterButton = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const handleClick = () => {
setCount(count + 1)
}
return (
<button onClick={handleClick}>
Number of clicks: {count}
</button>
)
}
<!-- Vue3 -->
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
const count = ref(0)
const incrementCount = () => {
count.value++
}
</script>
<template>
<button @click="incrementCount">
Number of clicks: { { count }}
</button>
</template>
<!-- svelte -->
<script>
let count = 0
const incrementCount = () => {
count++
}
</script>
<button on:click={incrementCount}>
Number of clicks: {count}
</button>
| Advantages of Svelte | Description |
|---|---|
| Writing Style | Easy to write based on the existing HTML, CSS, and JavaScript structure (similar to Vue) |
| Code Size | Allows writing smaller and cleaner code compared to other frameworks |
| Reactivity | Provides fast reactivity without using a virtual DOM |
| Bundle Size | Generates a smaller bundle size during build, which helps overcome the drawbacks of SPA (Single Page Application) |
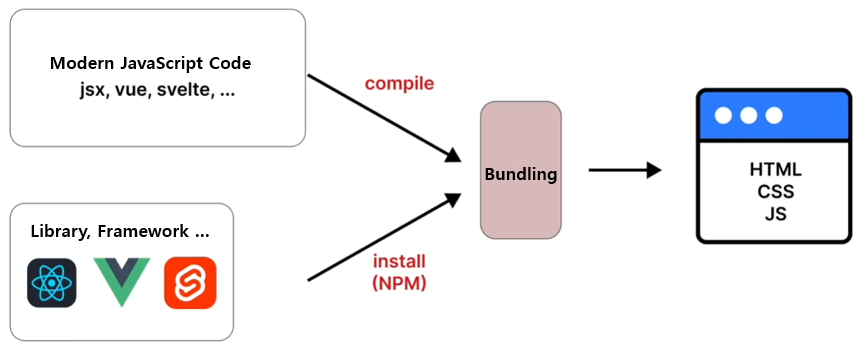 Bundling(Source: csslink)
Bundling(Source: csslink)
Bundling is the process of combining and optimizing files and modules used during development into a single file that can be executed by the browser. The size of the bundle can directly impact the page load time.
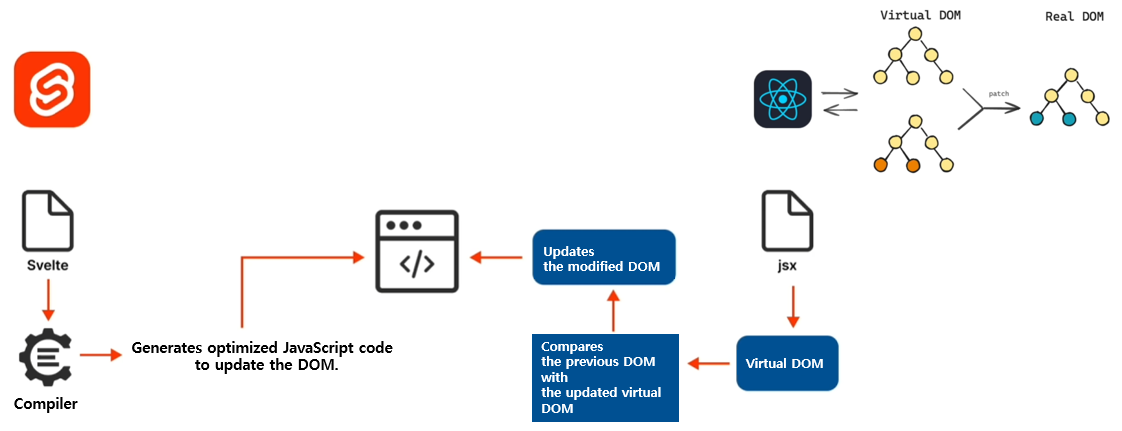 Process update the DOM(Source: csslink)
Process update the DOM(Source: csslink)
The DOM (Document Object Model) is a tree-structured object model that allows a web page to be programmatically accessed and manipulated. In simple terms, it is a structured representation of a web page that enables the browser to understand its content and allows JavaScript to modify the page or handle events.
Looking more closely, the Virtual DOM refers to an in-memory representation of the actual DOM with the same structure and content. When an update occurs, the Virtual DOM checks for any changes and compares only the differences with the Real DOM. This approach helps minimize unnecessary rendering operations and improves performance. React and Vue both adopt the Virtual DOM technique. On the other hand, Svelte takes a different approach — it updates the Real DOM directly without using a Virtual DOM, resulting in faster and more efficient updates.
Introuduce SvelteKit
SvelteKit is a framework for rapidly developing robust, performant web applications using Svelte. If you’re coming from React, SvelteKit is similar to Next.js. If you’re coming from Vue, SvelteKit is similar to Nuxt.js.
Since SvelteKit is a web application framework built on top of Svelte, if you already have a good understanding of Svelte, you can focus mainly on routing and API features.
I’ll cover the details as I explore them through hands-on experience.
Underlying Framework
| Feature | Next.js | Nuxt.js | SvelteKit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Based on | React | Vue.js | Svelte |
| Language | JS/TS | JS/TS | JS/TS |
| Styling | CSS-in-JS, Tailwind, etc. | CSS Modules, Tailwind, etc. | Native CSS, Tailwind, etc. |
Build & Deployment
| Feature | Next.js | Nuxt.js | SvelteKit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Build Command | next build | nuxt build | vite build (via SvelteKit) |
| Run Command | next start | nuxt start | node build (via adapter-node) |
| Static Deployment | next export | nuxt generate | Use adapter-static |